TAGNN-PP
TAGNN-PP models item interactions with GNN, and both local and global user interactions with a Transformer.
research paper
Session-based recommendation systems suggest relevant items to users by modeling user behavior and preferences using short-term anonymous sessions. Existing methods leverage Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) that propagate and aggregate information from neighboring nodes i.e., local message passing. Such graph-based architectures have representational limits, as a single sub-graph is susceptible to overfit the sequential dependencies instead of accounting for complex transitions between items in different sessions. We propose using a Transformer in combination with a target attentive GNN, which allows richer Representation Learning. Our experimental results and ablation show that our proposed method is competitive with the existing methods on real-world benchmark datasets, improving on graph-based hypotheses.
Architecture
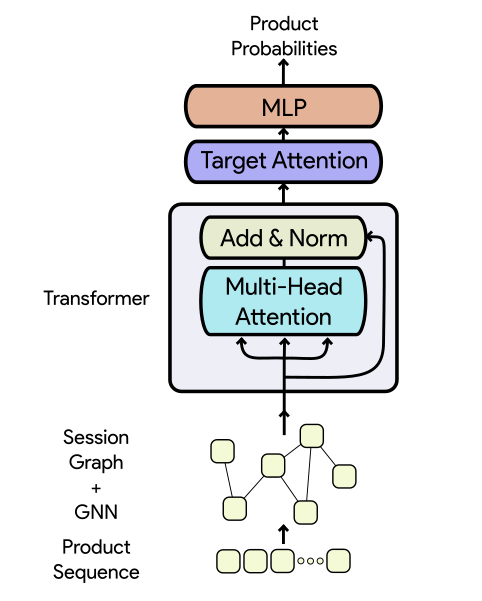
Architecture of a closely-matching model (for better understanding)
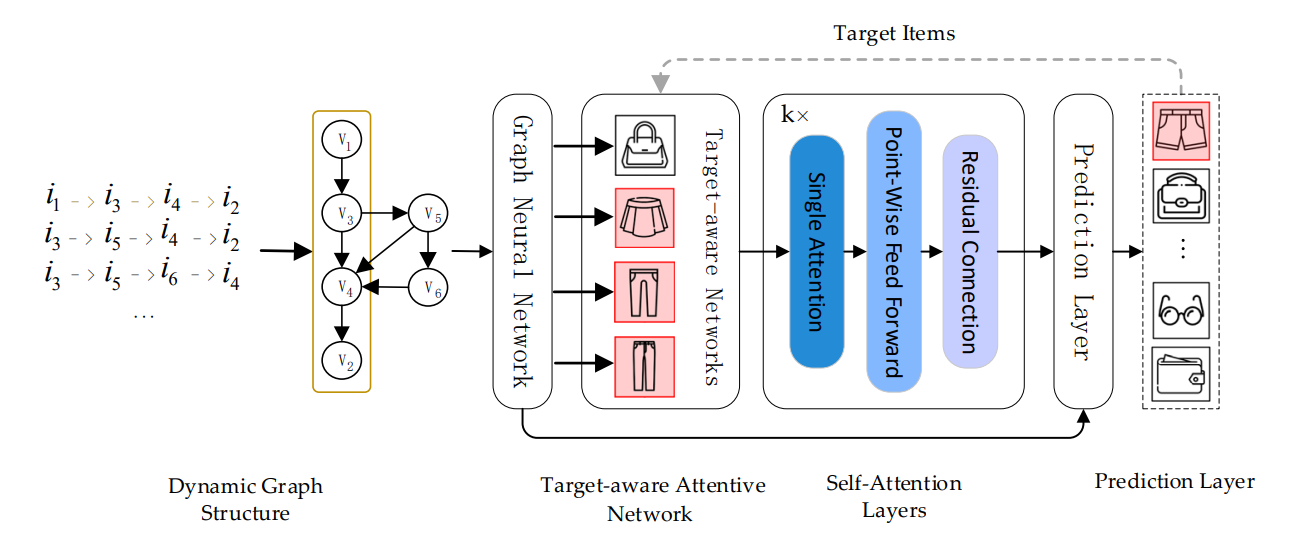
We first model user’s interaction sequences as session graphs which serves as the input of the graph neural network, and we can obtain each node vector involved in session graph via graph neural network. Next, target attentive network activates different user interests corresponding to varied target items adaptively (i.e., the learned interest representation vector varies with different target items). Then, we leverage the self-attention mechanism to accurately capture users’ long-term interests. Finally, we combine long-term and short-term interests to infer the probabilities for each candidate item for recommendation task.
Implementation
PyTorch Implementation (forward method)
def forward(self, inputs, A):
hidden = self.embedding(inputs)
hidden = self.tagnn(A, hidden)
hidden = hidden.permute(1, 0, 2)
skip = self.layer_norm1(hidden)
hidden, attn_w = self.attn(
hidden, hidden, hidden, attn_mask=get_mask(hidden.shape[0]))
hidden = hidden+skip
hidden = hidden.permute(1, 0, 2)