SR-SAN
SR-SAN stands for Session-based Recommendation with Self-Attention Networks.
research paper
Jun Fang, “Session-based Recommendation with Self-Attention Networks”. arXiv, 2021.
Session-based recommendation aims to predict user's next behavior from current session and previous anonymous sessions. Capturing long-range dependencies between items is a vital challenge in session-based recommendation. A novel approach is proposed for session-based recommendation with self-attention networks (SR-SAN) as a remedy. The self-attention networks (SAN) allow SR-SAN capture the global dependencies among all items of a session regardless of their distance. In SR-SAN, a single item latent vector is used to capture both current interest and global interest instead of session embedding which is composed of current interest embedding and global interest embedding. Some experiments have been performed on some open benchmark datasets. Experimental results show that the proposed method outperforms some state-of-the-arts by comparisons.
Firstly, a self-attention based model which captures and reserves the full dependencies among all items regardless of their distance is proposed without using RNNs or GNNs. Secondly, to generate session-based recommendations, the proposed method use a single item latent vector which jointly represents current interest and global interest instead of session embedding which is composed of current interest embedding and global interest embedding. In RNNs or GNNs based methods, the global interest embedding usually obtained by aggregating all items in the session with attention mechanism which is based on current interest embedding. However, this is redundant in SR-SAN which last item embedding is aggregating all items in the session with self-attention mechanism. In this way, the last item embedding in session can jointly represent current interest and global interest.
It utilizes the self-attention to learn global item dependencies. The multi-head attention mechanism is adopted to allow SR-SAN focus on different important part of the session. The latent vector of the last item in the session is used to jointly represents current interest and global interest with prediction layer.
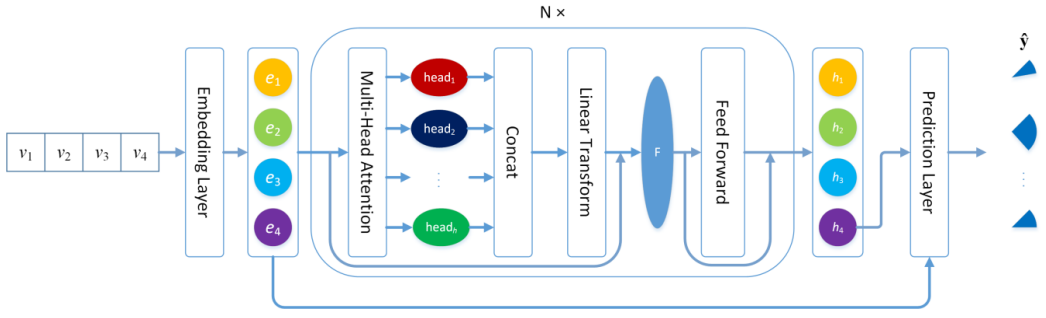
The architecture of SR-SAN.
Session-based recommender system makes prediction based upon current user sessions data without accessing to the long-term preference profile. Let denote the set consisting of all unique items involved in all the sessions. An anonymous session sequence can be represented by a list , where represents a clicked item of the user within the session . The task of session-based recommendation is to predict the next click for session . Our models are constructed and trained as a classifier that learns to generate a score for each of the candidates in . Let denote the output score vector, where corresponds to the score of item . The items with top-K values in will be the candidate items for recommendation.
The proposed model is made up of two parts. The first part is obtaining item latent vectors with self-attention networks, the second part of the proposed model is making recommendation with prediction layer.