AFM
AFM stands for Attentional Factorization Machines. It Improves FM by discriminating the importance of different feature interactions, and learns the importance of each feature interaction from data via a neural attention network. Empirically, it is shown on regression task that AFM performs betters than FM with a 8.6% relative improvement, and consistently outperforms the state-of-the-art deep learning methods Wide&Deep and DeepCross with a much simpler structure and fewer model parameters.
research paper
Factorization Machines (FMs) are a supervised learning approach that enhances the linear regression model by incorporating the second-order feature interactions. Despite effectiveness, FM can be hindered by its modelling of all feature interactions with the same weight, as not all feature interactions are equally useful and predictive. For example, the interactions with useless features may even introduce noises and adversely degrade the performance. In this work, we improve FM by discriminating the importance of different feature interactions. We propose a novel model named Attentional Factorization Machine (AFM), which learns the importance of each feature interaction from data via a neural attention network. Extensive experiments on two real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of AFM. Empirically, it is shown on regression task AFM betters FM with a 8.6% relative improvement, and consistently outperforms the state-of-the-art deep learning methods Wide&Deep and DeepCross with a much simpler structure and fewer model parameters.
Architecture
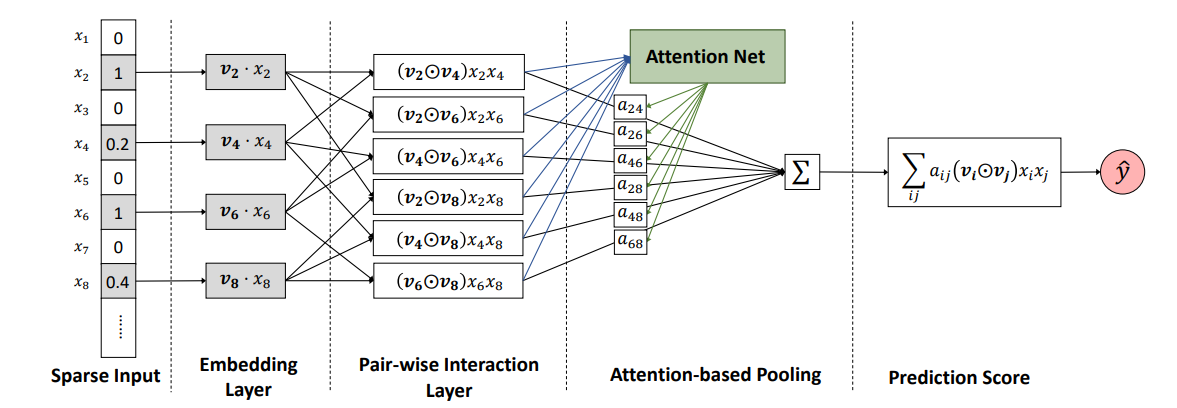
Formally, the AFM model can be defined as: