SASRec
SASRec stands for Self-Attentive Sequential Recommendation. It relies on the sequence modeling capabilities of self-attentive neural networks to predict the occurence of the next item in a user’s consumption sequence. To be precise, given a user 𝑢 and their time-ordered consumption history SASRec first applies self-attention on followed by a series of non-linear feed-forward layers to finally obtain the next item likelihood.
research paper
Wang-Cheng Kang and Julian McAuley, “Self-Attentive Sequential Recommendation”. ICDM, 2018.
Sequential dynamics are a key feature of many modern recommender systems, which seek to capture the ‘context’ of users’ activities on the basis of actions they have performed recently. To capture such patterns, two approaches have proliferated: Markov Chains (MCs) and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs). Markov Chains assume that a user’s next action can be predicted on the basis of just their last (or last few) actions, while RNNs in principle allow for longer-term semantics to be uncovered. Generally speaking, MC-based methods perform best in extremely sparse datasets, where model parsimony is critical, while RNNs perform better in denser datasets where higher model complexity is affordable. The goal of our work is to balance these two goals, by proposing a self-attention based sequential model (SASRec) that allows us to capture long-term semantics (like an RNN), but, using an attention mechanism, makes its predictions based on relatively few actions (like an MC). At each time step, SASRec seeks to identify which items are ‘relevant’ from a user’s action history, and use them to predict the next item. Extensive empirical studies show that our method outperforms various state-of-the-art sequential models (including MC/CNN/RNN-based approaches) on both sparse and dense datasets. Moreover, the model is an order of magnitude more efficient than comparable CNN/RNN-based models. Visualizations on attention weights also show how our model adaptively handles datasets with various density, and uncovers meaningful patterns in activity sequences.
Architecture
Sequential dynamics are a key feature of many modern recommender systems, which seek to capture the ‘context’ of users’ activities on the basis of actions they have performed recently. To capture such patterns, two approaches have proliferated: Markov Chains (MCs) and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs). Markov Chains assume that a user’s next action can be predicted on the basis of just their last (or last few) actions, while RNNs in principle allow for longer-term semantics to be uncovered. Generally speaking, MC-based methods perform best in extremely sparse datasets, where model parsimony is critical, while RNNs perform better in denser datasets where higher model complexity is affordable. SASRec captures the long-term semantics (like an RNN), but, using an attention mechanism, makes its predictions based on relatively few actions (like an MC).
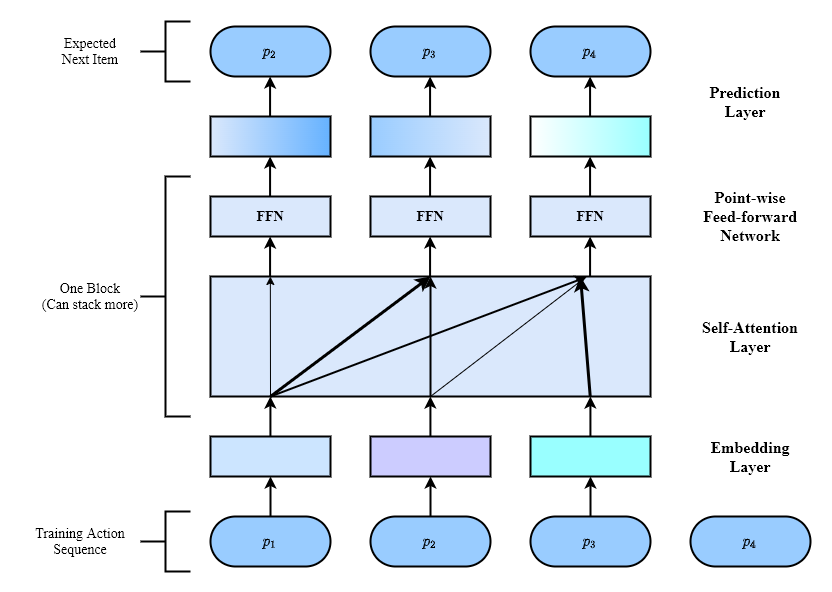
At each time step, SASRec seeks to identify which items are ‘relevant’ from a user’s action history, and use them to predict the next item. Extensive empirical studies show that this method outperforms various state-of-the-art sequential models (including MC/CNN/RNN-based approaches) on both sparse and dense datasets. Moreover, the model is an order of magnitude more efficient than comparable CNN/RNN-based models.
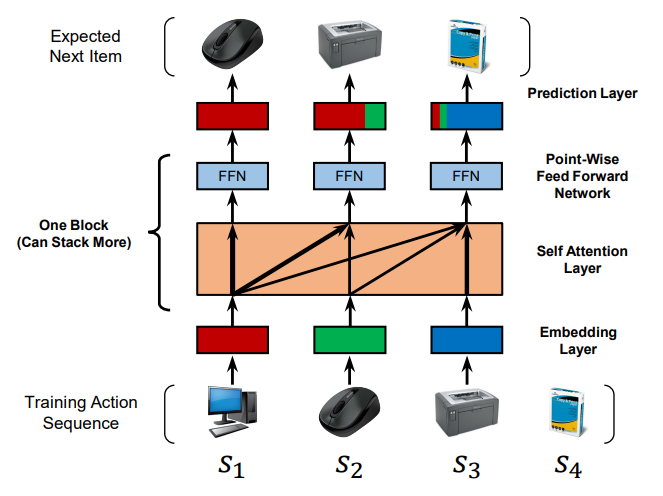
A simplified diagram showing the training process of SASRec. At each time step, the model considers all previous items, and uses attention to ‘focus on’ items relevant to the next action.
We adopt the binary cross entropy loss as the objective function: