Scribd Real-time
Transformer based model architecture can be applied to recommendation applications as well but recommendation problems are a bit more complex than NLP domain so it needs to be adapted according to the business needs. Therefore, instead of predicting next word based on the past sequence of words, at Scribd, we are interested in predicting what user would like to read next based on rich user interaction history with multiple types of documents and multiple types of interactions, where position in sequence & relative time are both important factors.
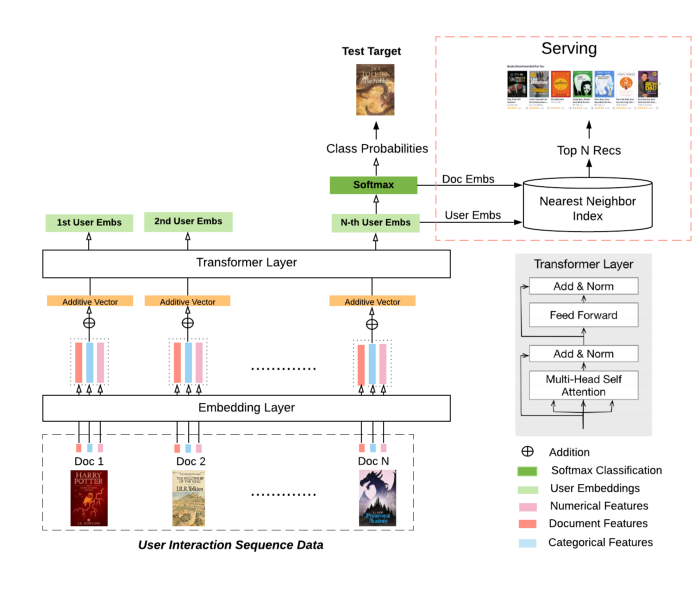
Model Architecture
We only used encoders of transformer architecture which uses self-attention to combine signals from users’ past interactions. Self-attention is pretty effective mechanism to capture any recent change in user’s interests and also preserving long term context at the same time. But our model still had popularity bias and we reduced it by stratifying training data.
Results
Using Scribd’s internal A/B testing platform, we conducted an experiment comparing the existing recommendations service with the new personalization model to generate subscribers’ home page. The test ran for approximately a month with >1M Scribd users (trialers or subscribers) assigned as participants. After careful analysis of results, we saw the following statistically significant (p<0.01) improvements in the personalization variant compared to the control experience across all user segments:
- Increase in the number of users who clicked on a recommended item
- Increase in the average number of clicks per user
- Increase in the number of users with a read time of at least 10 minutes (in a three day window)
- These increases represent significant business impact on key performance metrics.