Santander Banking Products
The goal of the bank is to predict which new products customers will purchase. The data starts on 2015–01–28, and has monthly records of the products each customer has, such as a credit card, savings account, etc. In addition, the dataset also records user personal data such as average income, age, gender, and so on. The monthly statistics are provided until 2015–05–28. Finally, the model predicts which additional products a customer will start using from the following month, 2016–06–28. Thus, the dataset spans 17 months from 2015–01–28 to 2016–05–28, and the output set contains only the timestamp corresponding to 2016–06–28. Models are therefore trained on sequences of 16 months to predict products acquired on their respective last month.
In this article, Genify discussed their approach towards this use case. They first used XGBoost for feature importance and selected the following features:
- Seniority: (integer in range 0–255) how long the user is a client of the bank;
- Age: (integer) age of the user;
- Segmentation: (category) status of the user: “01-VIP”, “02 -Individuals”, “03 -college graduated”.
- Gross household income: (integer) user’s yearly income based on his region of residence.
As part of preprocessing, they normalized the integer values and one-hot encoded the segmentation categories. Missing values are filled with mean. To make it clearer, let’s represent how a “word” of the sequence would look like after pre-processing.
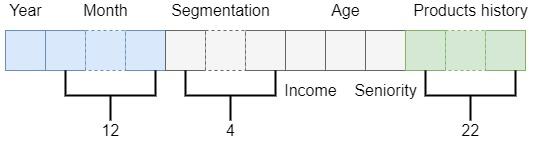
Note that, except for “Gross household income,” “Age,” and “Seniority,” all features are binary, and their concatenation forms a 42 elements array. Finally, the input to the model is a sequence formed by 16 words grouped in batches of 32.
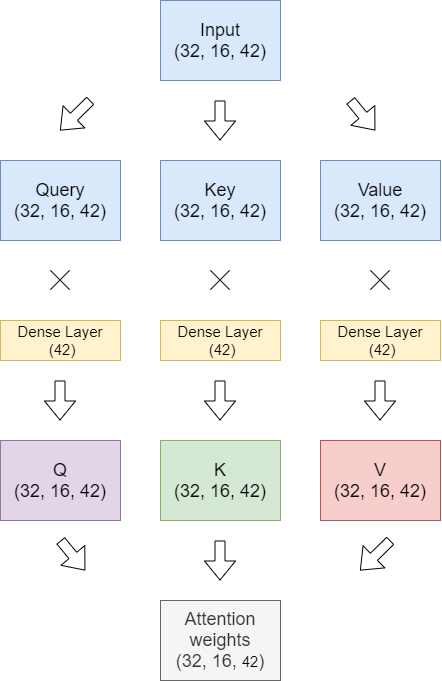
Model Architecture.
The model takes a sequence of 16 months of user’s history as an input and learns to predict the items acquired in the very last month. The model is composed of 6 multi-head encoder attention layers with 7 attention heads.
Each of those layers is followed by a 2048 size feed-forward layer. Before each attention and feed-forward layer we have a batch-normalization layer. After each layer, we have a dropout layer with a dropout chance of 0.5 to reduce overfitting. On top of the encoder we have a feed-forward layer followed by a softmax layer, which are used to predict the probability of an item owned in the last month. An item is considered as owned if it probability is > 0.5. Similarly, acquired items can be predicted by excluding the items owned in the previous month from the original predictions. Therefore, the model learns using a binary cross entropy loss function and Adam as optimizer. Regarding the learning rate, they adopted a Rectified-Adam warm-up scheduling for the learning rate, with a peak after 10 epochs and decay until the 100th epoch when the training process terminates. Having a warm-up scheduling assures to have a higher learning rate at the beginning of the training when the parameters of the model are still far from the optimum. After a certain peak it gradually decreases to provide a more stable training.